
Garlic
Garlic is a natural antibiotic, antifungal and strong antiviral. The most important properties of garlic are related to allicin, allicin is an oily, light yellow compound that creates a special garlic aroma. Allicin is also called garlic oil.
Garlic has been used for blood purification for many years. Garlic contains sulfur compounds that stimulate the immune system and have a high potential for destroying cancerous tumors.
Eating garlic clears the airways and clears the blood, reducing the severity of shortness of breath and sometimes treating it.
The smell of garlic is relieved by chewing lettuce, parsley or eating milk, apples or honey. Also, putting some dry tea in your mouth and swallowing it is effective in eliminating the bad smell of garlic.
Garlic is useful for treating various ailments such as asthma, bronchitis, rheumatism, gout, corns and warts (topically), tuberculosis, toothache, stinging and high blood pressure. It also crushes kidney stones and is effective in disinfecting urinary tract and vaginal and bladder infections.
Sulfur and selenium prevent the tumor and reduce its size if the tumor develops.
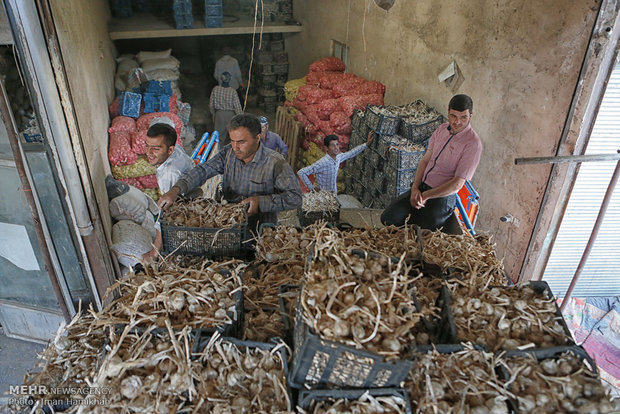
Hird khazar Export Garlic Specifications
Type : Garlic
Packaging : Customised packing based on your order
Garlic has analgesic properties and treats toothache.
It regulates blood sugar by raising insulin levels.
Its powerful antioxidant neutralizes free radicals that cause aging and disease.
By diluting the blood, it prevents the blood from clotting, thus reducing the risk of stroke.
Garlic is one of the most important popular products in Iran due to its type of planting, holding and harvesting, and it is in the production basket of agricultural products and export basket with very high added value.
Russia, the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, Turkey, Iraq and the United Arab Emirates are Iran’s export destinations.
Garlic is planted from the first cold of the region until the end of November. Planting garlic in the spring will reduce the size of the garlic, and it may germinate before winter and destroy the cold.
Usually, you have to wait until mid-spring or early summer to export fresh garlic, depending on the cultivated area. Otherwise, dried garlic should be exported.
Direct sunlight spoils the garlic, and the heat helps the garlic to smell better. Hang uncooked garlic cloves in the wire basket in the corner of your kitchen or juicer and out of direct sunlight.
It is best to place the garlic in a cool, dry place or in the refrigerator and use as needed. If you use a refrigerator, keep them in a plastic bag with a zipper so that the odor does not spread inside the refrigerator
Allium sativum: facts and myths regarding human health
Free article
Abstract
Garlic (Allium sativum L. fam. Alliaceae) is one of the most researched and best-selling herbal products on the market. For centuries it was used as a traditional remedy for most health-related disorders. Also, it is widely used as a food ingredient–spice and aphrodisiac. Garlic’s properties result from a combination of variety biologically active substances which all together are responsible for its curative effect. The compounds contained in garlic synergistically influence each other so that they can have different effects. The active ingredients of garlic include enzymes (e.g. alliinase), sulfur-containing compounds such as alliin and compounds produced enzymatically from alliin (e.g. allicin). There is a lot of variation among garlic products sold for medicinal purposes. The concentration of Allicin (main active ingredient) and the source of garlic’s distinctive odor depend on processing method. Allicin is unstable, and changes into a different chemicals rather quickly. It’s documented that products obtained even without allicin such as aged garlic extract (AGE), have a clear and significant biological effect in immune system improvement, treatment of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, liver and other areas. Some products have a coating (enteric coating) to protect them against attack by stomach acids. Clinically, garlic has been evaluated for a number of purposes, including treatment of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, cold or the prevention of atherosclerosis and the development of tumors. Many available publications indicates possible antibacterial, anti-hypertensive and anti-thrombotic properties of garlic. Due to the chemical complexity of garlic and the use of different processing methods we obtain formulations with varying degrees of efficacy and safety
Quantitative determination of allicin in garlic: supercritical fluid extraction and standard addition of alliin
Abstract
A quantitative method is described for the determination of allicin (2-propene-1-sulfinothioic acid S-2-propenyl ester) in garlic, using standard additions of alliin (l-(+)-S-allylcysteine sulfoxide) in conjunction with supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) and high performance liquid chromatography analysis with UV-vis absorbance detection. Optimum CO(2)-SFE conditions provided 96% recovery for allicin with precision of 3% (RSD) for repeat samples. The incorporation of an internal standard (allyl phenyl sulfone) in the SFE step resulted in a modest improvement in recovery (99%) and precision (2% RSD). Standard additions of alliin were converted to allicin in situ by endogenous alliinase (l-(+)-S-alk(en)ylcysteine sulfoxide lyase, EC 4.4.1.4). Complete conversion of the spiked alliin to allicin was achieved by making additions after homogenization-induced conversion of the naturally occurring cysteine sulfoxides to thiosulfinates had taken place, thus eliminating the likelihood of competing reactions. Concentration values for allicin determined in samples of fresh garlic (Allium sativum L. and Allium ampeloprasum) and commercially available garlic powders (Allium sativum L.) by standard addition of alliin were found in all cases to be in statistical agreement (95% confidence interval) with values determined using a secondary allicin standard (concentration determined using published extinction coefficients). This method provides a convenient alternative for assessing the amount of allicin present in fresh and powdered garlic, as alliin is a far more stable and commercially prevalent compound than allicin and is thus more amenable for use as a standard for routine analysis.
Quality of herbal remedies from Allium sativum: differences between alliinase from garlic powder and fresh garlic
Abstract
Alliinase (EC 4.4.1.4) has been isolated from commercially available garlic (Allium sativum L., Alliaceae) powder and was investigated with respect to its use as ingredient of herbal remedies. The enzyme was purified to apparent homogeneity and results were compared with those obtained from a sample of fresh A. sativum var. pekinense. The purification of the enzyme involved a gel filtration step as well as affinity chromatography on concanavalin-A agarose. Vmax using L-(+)-alliin as substrate (252 mumol min-1 mg-1) was at the lower range of data given in the literature (214-390 mumol min-1 mg-1). L-(-)-Alliin was also accepted as substrate (54 mumol min-1 mg-1). Vmax for alliinase from A. sativum var. pekinense was at 332 mumol min-1 mg-1 and 90 mumol min-1 mg-1 for L-(+)- and L-(-)-alliin, respectively. The Km values for alliinase from garlic powder were estimated to be 1.6 mM for L-(+)-alliin and 2.8 mM for L-(-)-alliin. In contrast to literature values, both temperature and pH optima were somewhat higher (36 degrees C and pH 7.0 versus 33 degrees C and pH 6.5, respectively). The enzyme was found to be active in a range from pH 5 to pH 10. Gel electrophoresis gave evidence that the alliinase obtained from garlic powder consisted of two slightly different subunits with molecular weights of 53 and 54 kDa whereas alliinase obtained from fresh garlic consists of two identical subunits. It is assumed that the alliinase gets significantly altered during the drying process of garlic powder but is still capable to convert alliin to allicin.
Garlic (Allium sativum) Properties
Immune Booster: Garlic is known for its immune-boosting properties, thanks to its rich content of antioxidants and vitamins.
Heart Health: It can help lower blood pressure and reduce cholesterol levels, supporting cardiovascular health.
Anti-Inflammatory: Garlic has anti-inflammatory effects that can help with various health conditions.
Antibacterial: Its active compound, allicin, has natural antibacterial properties.
Antiviral: Garlic may help in fighting viral infections, including the common cold.
Antifungal: It can combat various fungal infections.
Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that garlic may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer.
Detoxification: Garlic supports the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Improved Digestion: It aids digestion by promoting the production of digestive enzymes.
Rich in Nutrients: Garlic contains essential vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, B6, and manganese.
Blood Sugar Control: It may help regulate blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for those with diabetes.
Skin Health: Garlic’s antioxidant properties can contribute to healthier skin.
Hair Health: It can help improve hair texture and strength.
Asthma Relief: Garlic’s anti-inflammatory effects may benefit individuals with asthma.
Wound Healing: Some people use garlic topically to promote wound healing.
Anti-aging: Its antioxidants can combat free radicals, potentially slowing down the aging process.
Mosquito Repellent: Garlic consumption can make your body less appealing to mosquitoes.
Bone Health: It may support bone health due to its calcium and vitamin C content.
Stress Reduction: Garlic can help the body cope with stress.
Flavorful Cooking: Besides its health benefits, garlic adds a delicious flavor to various dishes.
Remember that while garlic offers numerous health advantages, it’s essential to consume it in moderation as part of a balanced diet to avoid any adverse effects

Two main types of garlic are distinguished by their physical characteristics and suitable climate conditions:
- Hardneck Garlic (سیر سخت گردن) and its Suitable Climate
Hardneck garlic is probably the type of garlic you’re most familiar with. It produces larger cloves but may have fewer cloves per bulb compared to softneck varieties. Hardneck garlic plants can produce scapes in the spring, which are long, woody stems that should be pruned to encourage the growth of larger garlic bulbs.
One of the simplest ways to identify hardneck garlic is by its stem. Hardneck garlic has woody and firm stems. When you purchase it from a store, you’ve probably noticed a woody stem of about one or two inches, connecting the cloves.
These woody stems produce green scapes in the spring. It’s a good idea to cut off the scapes in the spring, as this encourages the plant to send more energy into growing larger garlic bulbs. Don’t discard the scapes, though; they can add a delicious flavor to your dishes.
For those living in cold climates, they often prefer to grow hardneck garlic, as it is firmer and can withstand the cold better. However, it takes longer for the garlic bulbs to mature. This is a trade-off worth considering because you can grow a wide variety of them, all of which have excellent flavors.
Softneck Garlic and its Suitable Climate
Softneck garlic is derived from hardneck garlic. It is a common type that you see in grocery stores because it matures more quickly. You can also find them in fruit markets.
Softneck garlic offers several advantages that make it an excellent choice for many gardeners. It is more adaptable to a wider range of climates, produces more cloves per plant, and doesn’t require the removal of scapes for desirable growth.
One key difference to note is that softneck garlic produces more cloves than hardneck garlic, but these cloves are smaller. The layers surrounding the cloves are papery and multi-layered, usually off-white to creamy, somewhat resembling parchment paper.
We’ve listed various types of hardneck and softneck garlic varieties here, allowing you to find suitable options for your garden.
The layers around the cloves are essential as they extend the shelf life. You can store them under the right conditions for up to eight months. If you wish to braid your garlic stems, you’ll want to grow softneck garlic. Braided garlic is both decorative and practical for storing and displaying the cloves.
Types of Hardneck Garlic and Their Unique Characteristics
First, let’s explore different varieties of hardneck garlic. You’ll produce a firm and robust central stem with hardneck garlic, and in the initial harvest, you’ll have garlic scapes. For those living in cold climates, hardneck varieties are often a better choice, and they usually have a superior taste.
Asian Hardneck Garlic (4-8 cloves, 5-6 months shelf life)
Notable Varieties: Asian Tempest, Pyongyang
Asian garlic originates from Korea and produces medium-sized bulbs with four to eight cloves in each bulb. Depending on the specific Asian garlic variety you grow, its taste can vary from sweet to spicy. Many Asian cuisines favor this type of garlic because it can add exceptional flavor and heat to your dishes.
One reason you might choose to grow an Asian variety is because, in the Hardneck category, this type stores very well. The average shelf life is five to six months, which is quite impressive.
Asian garlic has a bright white to dark purple, tall and wide-leaved foliage.
Mature plants can reach up to four feet in height. They require average moisture and should grow in full sun in well-drained and fertile soil.
Creole Garlic (Hardneck, 8-12 cloves, tropical regions)
Notable Varieties: Burgundy, Red Creole
If you live in a slightly warmer region, Creole garlic is an excellent choice. Gardeners throughout the southern United States grow this type, but it won’t thrive as well in colder, northern states.
When grown in ideal conditions, Creole Hardneck garlic produces small to medium-sized bulbs with eight to twelve cloves in each. You’ll notice a delightful, slightly spicy taste that quickly fades. Creole is a popular choice in delicious dishes thanks to its delectable flavor.
Mature green plants can grow up to six feet tall. Growing Creole garlic is easy. You need average moisture and should grow it in full sun with well-drained, fertile soil. At the end of the growing season, your bulbs will be vividly colored in red and purple hues.
Shiny Purple Stripe Garlic (Hardneck, 6-12 cloves, 5-7 months shelf life)
Notable Varieties: Metechi, Siberian, Red Rezan, Chesnok
Shiny Purple Stripe garlic hails from Russia and Eastern Europe, so you can expect it to thrive in a wide range of climates.
The (Marbled Purple Stripe) bulbs have a robust flavor, and each bulb contains four to eight cloves. The garlic cloves have a decorative appearance with red and cream-colored stripes and a glossy surface.
This variety stores well for an extended period, usually up to seven months. Most people consider it the best garlic for cooking due to its flavor.
Because the bulbs in this variety are more delicate, large-scale commercial production can be challenging.
Middle Eastern Garlic (Hardneck, Tropical Region, Rough Texture)
Notable Varieties: Syrian, Jomah (Syrian)
As the name suggests, Middle Eastern garlic hails from the Middle East and prefers growing conditions in warmer climates. They do not grow as large as some other varieties, reaching only about three feet in height.
Middle Eastern garlic has slender leaves, and the size of the bulbs varies. Most of the bulbs have a rough texture compared to others.
- Porcelain Garlic (2-6 cloves, 8-month shelf life, Hardneck)
Notable Varieties: Polish, German White, Georgian Crystal, Romanian Red
Porcelain (or hardneck) garlic is a popular type with various sub-varieties you can grow. All porcelain varieties produce large bulbs with two to six cloves. They are known for their medium to strong flavor and tall green scapes that can reach up to 6 feet in height.
If you want to grow a type of garlic with a traditional taste you love, Porcelain is a great choice. It’s an excellent option for cooking and is one of the most popular hardneck garlic types for enthusiastic chefs.
Porcelain got its name because it has very smooth, thick skin and is sometimes adorned with purple stripes. The skin of Porcelain resembles papery texture that glistens in the light. It has a maximum shelf life of eight months and stores well.
- Purple Stripe Garlic (8-16 cloves, sweet taste, Hardneck)
Notable Varieties: Chesnok Red, Shatili, Purple Star
Purple Stripe garlic hails from the Republic of Georgia and is famous for its rich flavor without being too pungent. When cooked, it becomes sweet in taste, so sweet that some people use it for making garlic ice cream (seriously!).
Purple Stripe garlic has narrow leaves and reaches a height of three to five feet. The cloves have purple streaks, and the bulbs are bronze. Each bulb can contain between 8 to 16 cloves.
- Rocambole Garlic (Hardneck, 6-month shelf life, prefers hot summers and cold winters)
Notable Varieties: Spanish Roja, Russian Red, German Red, Chesnok Red
This is one of the best garlic types for gardeners who want to grow hardneck garlic at home. Rocambole garlic has a full aroma and flavor with loose skin that makes it easy to peel.
Both gardeners and chefs consider Rocambole garlic to have one of the best flavors, but it can be a bit challenging to grow because it needs very cold winters.
The delicious flavor comes with a cost. Rocambole is a picky one when it comes to over-watering. If you have a moist year with abundant rainfall, don’t expect them to perform well. They also prefer warmer summers compared to other types.
Rocambole garlic is often yellow or red with hard skin, and the bulbs come in a double ring arrangement.
- Elephant Garlic (Softneck, 5-6 cloves, mild taste, Not a true garlic)
Notable Varieties: N/A
Elephant garlic is actually not a true garlic but belongs to the leek family. It produces large bulbs with very mild garlic flavor. The size of the cloves and bulbs is enormous compared to true garlic, and it has a significantly milder taste.
It’s often used in recipes to add a subtle garlic essence without the overpowering taste that true garlic can have. Elephant garlic can be a great choice for those who want a milder garlic flavor in their dishes.
Elephant garlic is often used in roasts, salads, and other dishes where a less intense garlic flavor is desired. It’s also a popular choice for garlic lovers who want a significant quantity of garlic with each clove.
Elephant Garlic (Hardneck, 4-6 Cloves, Mild Flavor)
Undoubtedly, no list of garlic varieties is complete without mentioning Elephant Garlic, often referred to as Buffalo Garlic. It’s the larger cousin of the garlic family, and while it’s technically garlic, it’s more closely related to leeks than to garlic.
You might be able to guess why they’re called elephants. They produce massive bulbs, with each bulb weighing up to a pound. Typically, each bulb contains 4 to 6 cloves. It’s a popular choice for its size and mild flavor, making it suitable for those who may not enjoy the strong taste of regular garlic.
Elephant garlic is a favorite because of its large cloves that are easy to peel, making it an excellent choice for chefs. Since its flavor is mild, it’s great for roasting, using in sauces, or adding to stir-fried dishes.
The only downside is that it can be challenging to grow in regions with shorter growing seasons, as the bulbs don’t have enough time to mature fully.
Softneck Garlic Types and Their Unique Characteristics
If you want to grow garlic types that allow you to braid the stems, you need Softneck garlic. There’s no need to trim the scapes in spring. Their flavor is milder.
French Red Garlic (12-25 Cloves, 10-Month Shelf Life, Softneck)
Notable Varieties: Italian Red, Red Toch, California Early
If you want to grow garlic that produces fewer but larger cloves, French Red garlic of the Softneck variety is for you. Bulbs usually hold between 12 to 25 cloves with an uneven pattern.
French Red garlic matures early in the season and adapts well to a wide range of climates and soil conditions. This is one of the reasons it’s a popular choice among home gardeners.
All French Red garlic features a slightly elongated, smooth bulb with silver-colored skin. This type can be stored for an extended period, up to ten months under suitable conditions.
Silver Skin Garlic (8-40 Cloves, Up to 12-Month Shelf Life, Softneck)
Notable Varieties: Polish White, Idaho Silver, Kettle River Giant
Compared to French Red Softneck garlic, Silver Skin garlic takes longer to mature fully, allowing for a wide range of clove sizes. Bulbs can contain anywhere from 8 to 40 cloves across five layers. That’s a lot of cloves!
Gardeners often find it frustrating to peel the tough skin of Silver Skin garlic, and their irregular sizes can make it easy to overlook some cloves. Nevertheless, Silver Skin is the most popular softneck garlic variety that you can find in grocery stores or farmer’s markets.
Most farmers grow Silver Skin for one reason, which is its long shelf life. It has the longest shelf life among all garlic types, allowing you to store it for up to 12 months.
What Is Black Garlic? Amazing Benefits of Black Garlic
You’re probably familiar with regular garlic, known for its strong odor and various health benefits. But have you ever heard of black garlic? Black garlic is regular white garlic that has undergone fermentation, and it offers up to four to five times more health benefits than regular garlic. Isn’t it great to be able to consume highly nutritious garlic every day without worrying about bad breath, while strengthening your immune system and maintaining good health?
What sets black garlic apart from white garlic (raw garlic)?
Why is the fermentation process necessary to transform white garlic into black garlic, and what benefits does fermented garlic provide? The most significant benefit is that black garlic loses its pungent odor and acquires a sweet and mellow flavor. In fact, eating black garlic is much easier and more enjoyable than consuming fresh or raw garlic. Black garlic has a sweet taste and a chewable texture, and it doesn’t have a strong odor.
The Difference Between Black Garlic and Fresh Garlic: Allicin
Black garlic has less allicin compared to fresh garlic. Allicin is a natural sulfur compound derived from garlic, which has various medicinal properties, including antiviral, antibacterial, antiparasitic, and antifungal effects. The pungent odor of garlic is due to allicin. In fact, this strong smell serves as a defense mechanism for the garlic plant, protecting it from predators and animals.
But what happens to this beneficial and pungent compound during the fermentation and transformation process of fresh garlic into black garlic? During fermentation, allicin is converted into antioxidants, compounds that enhance the therapeutic properties of garlic. While the amount of allicin decreases, the antioxidants in black garlic increase by 4 to 5 times. According to research, the fermentation and transformation process improves the health benefits of garlic for the human body. Additionally, the conversion of allicin into antioxidants eliminates the bad odor associated with garlic.
In summary, the differences between black garlic and fresh garlic include:
- Black garlic has 4 to 5 times the preventive and therapeutic properties (antioxidants) compared to fresh garlic.
- Black garlic is sweet and easier to consume, while fresh garlic has a strong and pungent taste.
- Unlike fresh garlic, black garlic does not have a bad odor.
- Black garlic has a soft, jelly-like texture.
- Fresh garlic contains more allicin.
- The color of black garlic is black, while fresh garlic is white.
Where Is Black Garlic Produced?
Black garlic is essentially regular garlic that has been fermented. It is not specific to any particular country, and black garlic can be produced in various regions. Black garlic is known as “black garlic” in English.
For centuries, people in East Asian countries such as Thailand, South Korea, and Japan have been producing black garlic. They have used black garlic as a flavor enhancer and for medicinal purposes. In recent years, this odorless and highly beneficial food has been produced and used worldwide.
Benefits of Black Garlic
Research has shown that black garlic is rich in antioxidants, which have strong anti-cancer properties. Additionally, the effects of black garlic include anti-allergic, anti-diabetic, and anti-inflammatory properties. In summary, the benefits of black garlic include:
Cancer prevention
Improved cancer treatment outcomes
Weight loss and weight management
Lowering blood cholesterol levels
Protecting the heart and blood vessels, preventing arteriosclerosis
Blood sugar control and diabetes prevention
Improved diabetes management and reduced complications
Anti-allergic effects
Reducing inflammation
Liver protection
If you ask, “What is black garlic good for?” we have a well-documented answer. The benefits mentioned for black garlic are based on scientific research, and the sources for each claim are provided in English.
The side effects of black garlic:
According to research, there are no significant or well-known side effects associated with black garlic. Regular consumption is considered safe and harmless. There have been no reports of adverse effects of black garlic on weight loss. It appears that the harm of black garlic is specific to harmful microorganisms and viruses.
Consuming black garlic can lower blood pressure. Therefore, individuals with naturally low blood pressure should consume black garlic along with foods that raise blood pressure; for example, they can consume salty foods or drink black garlic with one or two cups of water.
Keep in mind that excessive consumption of black garlic can have adverse effects. It has been established through research that excessive consumption of raw garlic can lead to poisoning. This issue applies to black garlic as well since the compounds in black garlic are similar to those in raw garlic. Therefore, it is recommended to consume one black garlic clove daily and not consume more than two cloves a day.
The process of black garlic fermentation:
The higher the temperature, the faster the black garlic fermentation process occurs. At 70 degrees Fahrenheit, garlic ferments at twice the speed compared to a temperature of 60 degrees. According to research, black garlic ferments better at temperatures between 70 to 80 degrees, leading to better quality, flavor, and color.
The water content in garlic is approximately 63%, which must be reduced to 40 to 50% during the fermentation process for better consumption. If the water content in garlic drops below this range, it will become dry and difficult to consume.
If garlic is fermented at temperatures between 80 to 90 degrees, the soluble sugar in it decreases, resulting in a lack of sweetness in the taste. Moreover, the hydroxymethylfurfural in the fermentation process increases, and this increase is less at a temperature of 60 degrees. Whether hydroxymethylfurfural is a beneficial or harmful substance is still a subject of debate among scientists. Previously, it was proven to have harmful properties, but recently, its beneficial properties, such as being an antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-allergy, and reducing damage caused by oxygen deficiency, have been established.
In conclusion, research indicates that the best temperature for fermenting garlic and transforming it into black garlic is 70 degrees Celsius. It’s important to note that temperature is not the only factor that matters, and the properties of black garlic are influenced by other factors such as humidity.

1Containing a Compound Called Allicin with Potential Medicinal Properties
Garlic is a plant from the Allium family, closely related to onions, leeks, and chives. It is cultivated in many parts of the world and is known for its strong aroma and delicious flavor, making it a popular seasoning in cooking. However, throughout ancient history, the primary use of garlic has been for its health and medicinal properties. Documentation of this can be found in various important civilizations, including the Egyptians, Babylonians, Greeks, Romans, and Chinese.
The entire “bulb” of garlic is referred to as a garlic head, and each individual segment of it is called a clove. A single garlic head typically contains around 10 to 20 cloves. It is now understood that the health benefits of garlic are attributed to its sulfur-containing compounds, which are released when garlic is crushed, chopped, or chewed. One of these compounds is called allicin, which is responsible for the distinct smell associated with garlic.
Allicin enters the body through the digestive system and is distributed throughout the body, exerting potent biological effects (which we will delve into shortly).
In summary, garlic is a plant from the onion family known for its culinary uses and valuable health benefits. Garlic is rich in a sulfur compound known as allicin, believed to be the source of many of its health benefits.

2Highly Nutritious yet Low in Calories
Each calorie in garlic is packed with an abundance of nutrients. For every 28 grams of garlic, you’ll find these essential nutrients:
Manganese: Providing 23% of your daily needs.
Vitamin B6: Supplying 17% of your daily requirements.
Vitamin C: Contributing 15% of your daily needs.
Selenium: Offering 6% of your daily needs.
Fiber: Providing 6 grams.
Adequate amounts of calcium, copper, potassium, phosphorus, iron, and vitamin B1.
Additionally, garlic contains trace amounts of other essential nutrients. In fact, garlic encompasses a broad range of nutrients that our bodies require. All these benefits come with a mere 42 calories, along with 8.1 grams of protein and 9 grams of carbohydrates per 28 grams.
In summary, garlic is low in calories but rich in vitamin C, vitamin B6, and manganese, along with substantial amounts of other necessary minerals and vitamins.
.3Benefits of Garlic for Treating the Common Cold
.4Blood Pressure Reduction
5Lowering the Risk of Heart Diseases
.6Promoting Longevity
.7Alzheimer’s and Memory Prevention
.8Enhancing Athletic Performance
.9Detoxifying the Body from Heavy Metals
.10Garlic’s Benefits for Bone Health
11Garlic’s Benefits for the Liver; Protecting the Liver from Alcohol-Related Damage
.12Strong Antibacterial Properties
.13Preventing Osteoarthritis
.14Treating Yeast Infections
15Preventing Tooth Decay and Treating Oral Infections

16Helping Treat HIV Infections
.17Assisting in Healing Ulcers Caused by Helicobacter pylori
.18Aiding in Treating Intestinal Infections Caused by Parasites
.19Cancer Prevention and Supportive Treatment
.20Garlic Benefits for Men; Reducing the Risk of Prostate Cancer
.21Garlic Benefits for Women; Preventing Breast Cancer Progression
.22Garlic Benefits for the Stomach; Preventing Stomach Cancer Progression
23Preventing Colorectal Cancer Progression
24Preventing Bladder Cancer27Anti-Aging Properties
25Assisting in Allergy Treatment
.26Garlic Benefits for the Skin; Protecting the Skin from Ultraviolet Rays
27Anti-Aging Properties

28Assisting in Treating Skin Lesions
.29Aiding in Wound Healing
30Garlic Benefits for Hair; Helping Reduce Hair Loss or Dandruff

31Reducing Cholesterol Levels
.32Preventing Obesity
33Assisting in Diabetes Management

34Enhancing Memory
.35Incredibly Delicious Flavor and Easy to Use
:Harvesting Garlic


















































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.